Hair loss (alopecia) can impact just your scalp or your whole body, and it can be momentary or permanent. It can be the outcome of heredity, hormone changes, medical conditions or a regular part of aging. Anyone can lose hair on their head, however it's more common in males.
Baldness typically describes excessive loss of hair from your scalp. Hereditary loss of hair with age is the most common reason for baldness. Some people choose to let their hair loss run its course without treatment and unhidden. Others might cover it up with hairstyles, makeup, hats or headscarfs. And still others select among the treatments offered to avoid further loss of hair or restore development.
Prior to pursuing hair loss treatment, talk with your medical professional about the cause of your loss of hair and treatment options.Symptoms
Hair loss can appear in various ways, depending upon what's causing it. It can begin suddenly or slowly and impact just your scalp or your entire body.
Symptoms and signs of loss of hair may include:
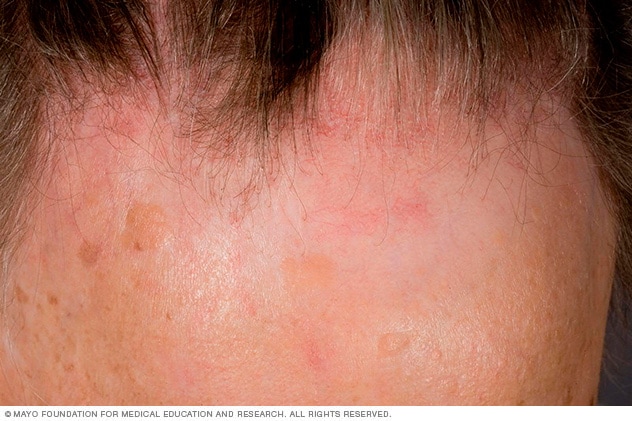
Steady thinning on top of head. This is the most common kind of loss of hair, affecting individuals as they age. In males, hair frequently starts to decline at the hairline on the forehead. Ladies typically have an expanding of the part in their hair. A significantly common loss of hair pattern in older females is a receding hairline (frontal fibrosing alopecia).
Circular or irregular bald areas. Some people lose hair in circular or patchy bald areas on the scalp, beard or eyebrows. Your skin may become scratchy or painful prior to the hair falls out.
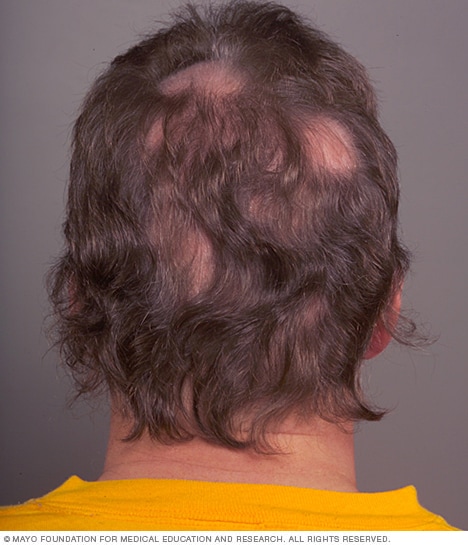
Abrupt loosening of hair. A physical or emotional shock can trigger hair to loosen up. Handfuls of hair may come out when combing or washing your hair or perhaps after gentle pulling. This kind of loss of hair usually triggers total hair thinning but is short-term.
Full-body loss of more info hair. Some conditions and medical treatments, such as chemotherapy for cancer, can lead to the loss of hair all over your body. The hair normally grows back.
Patches of scaling that spread over the scalp. This suggests ringworm. It may be accompanied by broken hair, inflammation, swelling and, sometimes, oozing.
When to see a physician
See your physician if you are distressed by relentless hair loss in you or your child and wish to pursue treatment. For females who are experiencing a declining hairline (frontal fibrosing alopecia), talk with your doctor about early treatment to avoid considerable irreversible baldness.
Also speak with your medical professional if you see sudden or patchy hair loss or more than normal loss of hair when combing or washing your or your child's hair. Unexpected loss of hair can signify a hidden medical condition that requires treatment.
Request a Visit at Mayo Center
Triggers Individuals typically lose 50 to 100 hairs a day. This typically isn't visible since brand-new hair is growing in at the same time. Hair loss happens when brand-new hair does not replace the hair that has fallen out. Family history (heredity). The most common cause of loss of hair is a genetic condition that occurs with aging. This condition is called androgenic alopecia, male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness. It generally occurs gradually and in predictable patterns-- a declining hairline and bald areas in males and thinning hair along the crown of the scalp in females.
Hormonal changes and medical conditions. A variety of conditions can cause long-term or momentary loss of hair, consisting of hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause and thyroid problems. Medical conditions include alopecia areata (al-o-PEE-she-uh ar-e-A-tuh), which is immune system associated and triggers irregular loss of hair, scalp infections such as ringworm, and a hair-pulling condition called trichotillomania (trik-o-til-o-MAY-nee-uh). Medications and supplements. Loss of hair can be a negative effects of particular drugs, such as those utilized for cancer, arthritis, anxiety, heart issues, gout and high blood pressure.
Radiation therapy to the head. The hair may not grow back the like it was previously.
A really demanding occasion. Many individuals experience a basic thinning of hair a number of months after a physical or psychological shock. This type of hair loss is short-term.
Hairstyles and treatments. Excessive hairstyling or hairdos that pull your hair tight, such as pigtails or cornrows, can trigger a kind of loss of hair called traction alopecia. Hot-oil hair treatments and permanents likewise can cause hair to fall out. If scarring happens, hair loss could be long-term.